When you do a search of what a virtual classroom is exactly, you come across a wide variety of definitions. Some of them relate the virtual classroom to course materials, homework, tests, and assignments that are typically used in self-paced (asynchronous) learning. However, all of these activities are external to the classroom experience. That is why the definition of a virtual classroom should be related to synchronous online learning, which happens in real time and provides the participants with an experience very close to traditional face-to-face teaching. Here is our understanding of what a virtual classroom is:
What is Virtual classroom
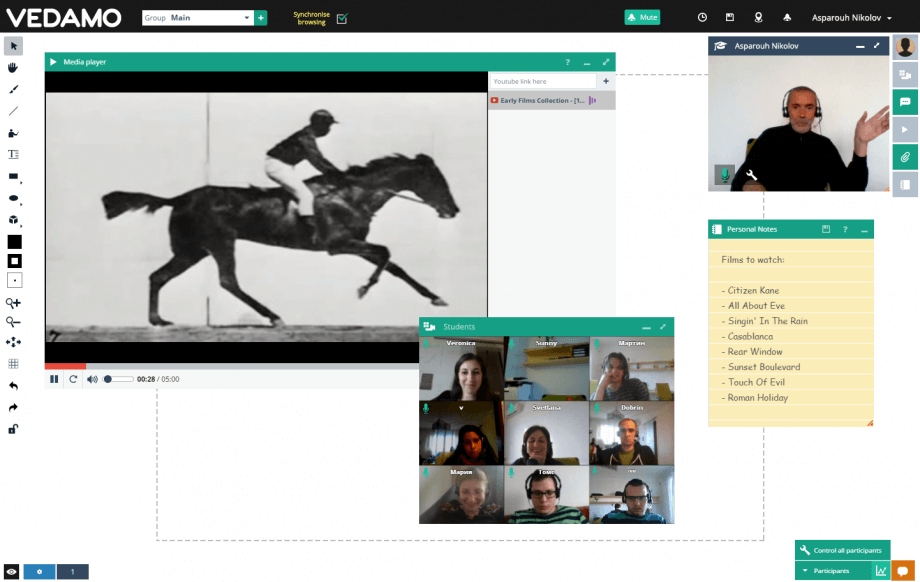
A virtual classroom is an online learning environment that allows for live interaction between the tutor and the learners as they are participating in learning activities.
In other words, the virtual classroom is a shared online space where the learners and the tutor work together simultaneously. Usually, these interactions take place through videoconferencing. The participants have tools to present learning content in different formats, as well as to implement collaborative and individual activities. In this type of interaction, the teacher has the particularly important role of the moderator who guides the learning process and supports group activities and discussions.
The most common tools you can find in a virtual classroom are:
- Videoconferencing
- Online whiteboard for real-time collaboration
- Instant messaging tool
- Participation controls
- Breakout rooms
Synchronous virtual classrooms have the potential to provide significant added value to online learning by addressing the needs of the learners as they relate to social interaction and psychological safety. They can also create a new standard in the learning experience that goes above and beyond the physical space of the classroom and traditional teaching methods.
The virtual classroom provides an abundance of opportunities, especially when combined with self-study platforms (learning management systems) or when used in addition to traditional classroom learning activities. Unlike asynchronous learning environments, the synchronous virtual classroom allows for instant feedback, direct teacher-student interaction, and engaging activities to increase motivation and active participation. Immediate communication favors relationship building within the group, as well as a sense of community.
Although teaching and learning in a virtual classroom provide an experience similar to the physical one, it requires new pedagogical approaches and a redesign of the instructional model that includes the following characteristics:
- Virtual Classroom’s high Interactivity
- Collaborative Learning
- Student-Centered Instruction
- Variety of Content Presentation and Learning Activities
- Psychologically Safe Environment
- Positive and Constructive Feedback
1. Virtual Classroom’s high Interactivity
Training in a synchronous virtual classroom can only be successful with the active participation and engagement of the learners. This creates a positive learning environment and helps the participants achieve the expected outcomes. During the virtual session there should be opportunities for frequent interaction between learner and tutor, learner and other learners, and learner and content. Over the course of the virtual session, the tutor should encourage the students to participate every 3-5 minutes. This can be achieved by a variety of activities such as brainstorming, small group discussion, collaborative and individual tasks, Q&A sessions, hands-on experience, etc.

2. Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning means that the learners work together to achieve a common goal, exchange views, clarify the meaning of concepts, or solve problems together. It creates opportunities for cooperation in skills development. The emphasis is placed on interaction in which common understandings are subject to discussion and are developed precisely through exploring the differences in the participants’ level of knowledge, skills, and positions. Applied in the virtual classroom, this approach is associated with an active process of the collective construction of knowledge using the group as a source of information, a motivational agent, and a means of mutual support.
3. Student-Centered Instruction
The lecture, which is a classic teaching format, often makes students more passive as the focus is on the content and the students must work independently with little opportunity for collaboration. This approach is more applicable to asynchronous virtual teaching – the tutor creates video lectures and self-directed activities, which the learners cover at their own pace. Synchronous virtual classes require student-centered instruction in which the learners and the tutor interact equally – active participation, collaborative work, and communication are encouraged in this type of classroom. The tutor creates opportunities for both independent learning and learning from one another, and guides the learners in developing and practicing the skills they need. This increases the motivation level of the learners, as well as their interest in the learning activities.

4. Variety of Content Presentation and Learning Activities
This approach is related to differentiated instruction, which takes into consideration the differences in the needs, levels, and learning styles of the learners. It favors the creation of a more personalized learning experience and individual success. When a teacher uses various sources to present the content – text, images, diagrams, audio, video, etc. – this can greatly improve the learning process by providing a flexible learning experience that is tailored to the various needs and preferences of the students. Presenting the content through various types of media retains the attention and interest of the learners.
Blending different types of learning activities within one virtual session also creates opportunities to meet a wider range of the needs of the students. Switching between individual work, small group collaboration, and class discussions addresses the specific learning preferences of all of the students – either to work alone, to interact with the others, or to express themselves in front of a larger group.
5. Psychologically Safe Environment
Interactions in a virtual classroom create the sense of a more informal and safer emotional environment as the learners usually participate from the comfort of their homes. The learning process is much more focused because of the absence of the usual physical distractions that are found in the conventional classroom.
Psychological safety leads to better learning outcomes. It also fosters creativity, confidence, and a willingness to experiment on the part of the learners. The virtual teacher also has a crucial role here – they need to encourage safe discussions, mutual respect, equal opportunities to participate, and the free sharing of different viewpoints. The teacher can enhance the psychological safety of the learners and make things more personalized by adding options for self-directed learning, as well as by communicating more frequently with every student through a Learning Management System.

6. Positive and Constructive Feedback
Unlike asynchronous virtual platforms, the synchronous virtual classroom allows for immediate feedback from both the tutor and the other participants in both an individual and a general way. The key role of the tutor here is to create an atmosphere of positive feedback by guiding the group’s interaction. The need for feedback, which acknowledges the positive aspects of the learners’ performance and gives valuable comments and recommendations for improvement, benefits the education and progress of the students. It also builds the habit in the group of trying to maintain a positive and constructive tone. All of these factors are vital in assisting the learners to overcome their mistakes without feelings of negativity, as well as by fostering confidence and inspiring them to achieve their full potential.

